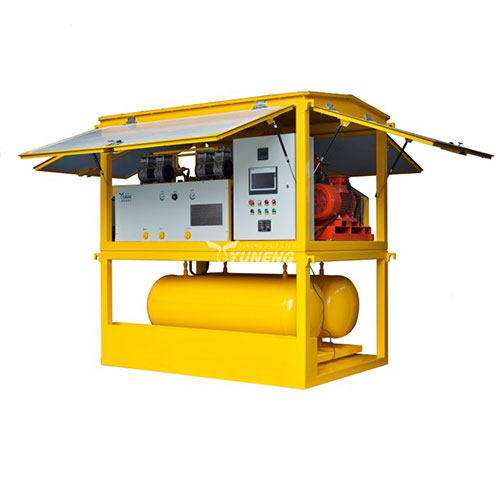
Comparison of SF6 Gas Recovery, Purification, and Refilling Equipment
Table of Contents
SF6 (sulfur hexafluoride) gas is widely used in electrical power systems, especially in high-voltage switchgear and gas-insulated substations (GIS), due to its excellent insulating properties and arc-quenching characteristics. However, SF6 is a potent greenhouse gas with a global warming potential (GWP) 23,900 times that of carbon dioxide. Therefore, the effective recovery, purification, and refilling of SF6 gas during equipment operation and maintenance are essential to minimize emissions, support environmental protection, and contribute to the sustainability of the industry.
In SF6 gas handling, recovery, purification, and refilling are the three key processes, each with distinct functions but closely related in design and application. This article aims to explore the similarities and differences between these three types of equipment, providing a deeper understanding of their roles and selection criteria.
Types of Functions in SF6 Gas Handling Equipment
1. SF6 Gas Recovery Equipment
The primary function of SF6 gas recovery equipment is to extract used SF6 gas from electrical equipment for storage and treatment. This typically occurs during maintenance, repair, or decommissioning of equipment. Since SF6 gas is often under high pressure, recovery equipment must efficiently and safely remove the gas from the equipment.
Features:
- Equipped with vacuum pumps and compressors to extract and compress gas into storage tanks.
- Typically includes basic filtration to remove moisture and some particulate impurities, though purification is limited.
- High recovery efficiency, often exceeding 99%, reducing gas leakage and waste.
Key Components:
- Vacuum pump: Reduces the internal pressure of the equipment, facilitating the removal of SF6 gas.
- Compressor: Compresses the recovered gas for storage in high-pressure tanks.
- Filter: Performs initial impurity filtration to prevent excessive contaminants from entering the storage tanks.
- Applications: SF6 gas recovery equipment is mainly used during the maintenance or decommissioning of electrical equipment, such as in GIS switchgear, ensuring both safety and environmental compliance.
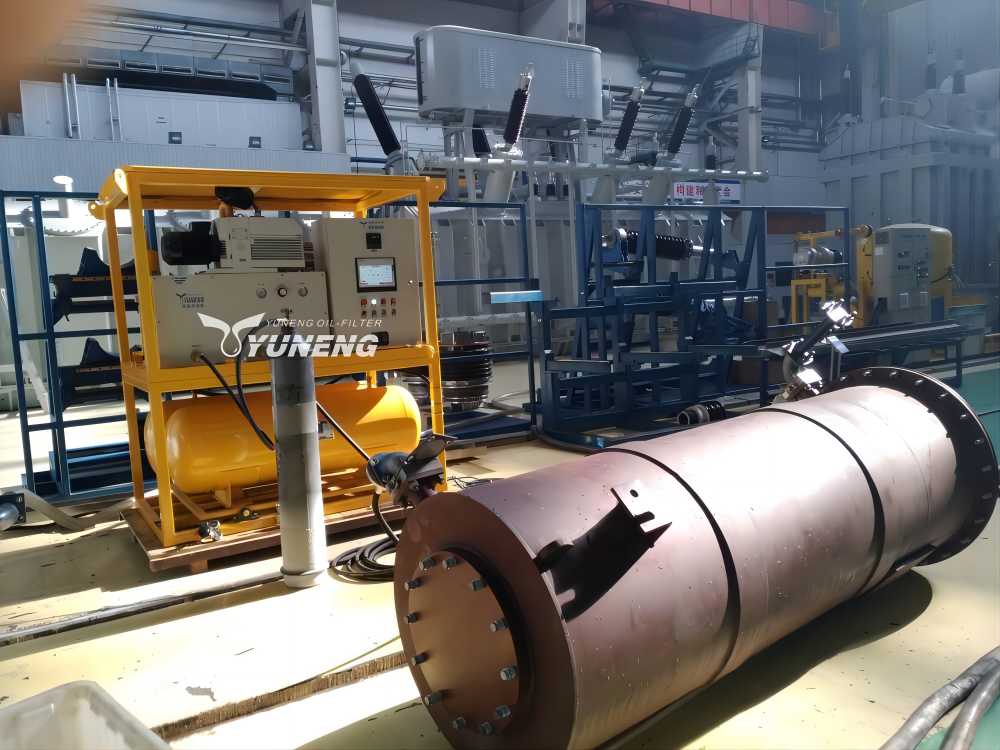

2. SF6 Gas Purification Equipment
Recovered SF6 gas often contains moisture, acidic compounds, and other contaminants resulting from decomposition products or external environmental factors. SF6 gas purification equipment processes the recovered gas to remove these impurities, ensuring that the gas meets purity standards for refilling.
Features:
- Includes multi-stage filtration systems such as drying units, molecular sieves, and chemical adsorption devices, efficiently removing moisture, acidic gases (e.g., SO2, HF), and particulates.
- Purified SF6 gas reaches purity levels above 99.99%, meeting stringent requirements for high-voltage equipment.
- Can be integrated with recovery equipment or used independently.
Key Components:
- Precision filters: Remove fine particulate matter, preventing wear and damage to equipment.
- Drying units: Use desiccants to remove moisture, lowering the gas’s dew point.
- Chemical adsorption devices: Absorb acidic compounds, reducing the corrosive nature of the gas.
- Applications: Purification equipment is essential when SF6 gas is being recycled or reused, particularly in centralized SF6 processing facilities or for immediate purification on-site.

3. SF6 Gas Refilling Equipment
After the installation, repair, or maintenance of electrical equipment, pure SF6 gas is required to refill the system to its nominal pressure. SF6 gas refilling equipment ensures the efficient and safe injection of SF6 into the equipment.
Features:
- Equipped with pressure control systems to adjust and maintain precise filling pressure for stable equipment operation.
- Refilling equipment does not have purification capabilities, so only purified SF6 gas can be used.
- Simple operation, allowing quick refilling of gas.
Key Components:
- Pressure regulating valve: Controls the flow and pressure of the gas during refilling.
- High-pressure hose: Transports the gas to the equipment.
- Precision pressure gauge: Monitors and displays the pressure during the refilling process.
Applications: SF6 gas refilling equipment is primarily used for the initial filling of new equipment and refilling after maintenance. For instance, new GIS switchgear installations require this equipment for their first gas fill.

Comparison of SF6 Gas Handling Equipment
The table below provides a detailed comparison of the three primary types of equipment used in the handling of SF6 gas: recovery, purification, and refilling. Each type serves a specific purpose in the lifecycle of SF6 gas within electrical equipment.
| Feature | SF6 Gas Recovery Equipment | SF6 Gas Purification Equipment | SF6 Gas Refilling Equipment |
| Primary Function | Extracts SF6 gas from electrical equipment for storage or further processing. | Removes impurities (moisture, acid, particulates) from recovered SF6 gas. | Introduces purified SF6 gas into electrical equipment to restore operating pressure. |
| Operating Principle | Creates a vacuum to draw gas out of the equipment, then compresses it for storage. | Employs various filtration and adsorption techniques to remove contaminants. | Regulates the flow of gas into the equipment to achieve the desired pressure. |
| Typical Components | Vacuum pump, compressor, storage tanks, basic filters. | Filters, dryers, molecular sieves, chemical adsorbers. | Pressure regulators, hoses, pressure gauges. |
| Process Integration | Often integrated with purification equipment to form a closed-loop system. | Can be integrated with recovery equipment for continuous processing. | Typically used in conjunction with purification equipment. |
| Performance Metrics | Recovery efficiency, gas purity (after initial filtration), and equipment downtime. | Purity of the treated gas, removal efficiency of specific contaminants, and throughput. | Filling accuracy, speed, and the ability to maintain a stable pressure. |
| Safety Considerations | Risk of gas leaks and equipment failure, requiring safety interlocks and alarms. | Potential for exposure to hazardous chemicals and the generation of waste. | Risk of overpressurization and equipment damage. |
The Trends of Integrated SF6 Gas Handling Equipment
With technological advancements, many manufacturers are integrating the recovery, purification, and refilling functions into a single device, creating comprehensive SF6 gas handling units.
Advantages
- Time and Space Efficiency: Integrated equipment can simultaneously handle recovery, purification, and refilling, greatly improving operational efficiency.
- Simplified Operation: Users do not need to switch between different machines, making operations more intuitive and convenient.
- Adaptability: Integrated equipment is more versatile and can be used in various field conditions, especially when space or equipment availability is limited.
Limitations
- Higher Cost: Integrated systems are typically more expensive than single-function equipment, making them suitable for users with larger budgets.
- Increased Maintenance Complexity: The high level of integration can lead to more complex maintenance and repairs, requiring specialized technical support.

Final Thoughts
- Recovery equipment acts as the first line of defense, preventing SF6 gas from being directly released into the atmosphere.
- Purification equipment is the core technology, ensuring that polluted gas can be reused safely.
- Refilling equipment is essential for maintaining optimal gas conditions inside electrical equipment.
As environmental regulations tighten and technology progresses, integrated systems are becoming the industry standard, improving operational efficiency and minimizing SF6 emissions. Moving forward, SF6 handling equipment will continue to evolve, becoming more efficient, intelligent, and environmentally friendly, contributing to the sustainable development of the power industry.







