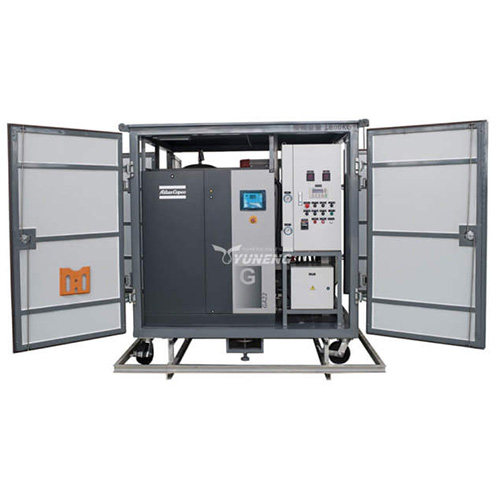
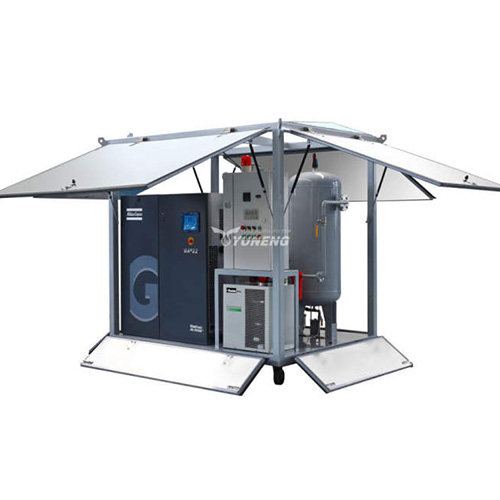
Dry Air Generators vs. Traditional Transformer Drying Methods: A Cost-Benefit Analysis
Transformers are vital components in electric power transmission and distribution systems. Their efficient operation relies heavily on maintaining proper insulation, which can be compromised by moisture. Regular drying is essential to remove moisture from transformers during maintenance or after fault events. This article analyzes two main drying methods: traditional methods and dry air generators, from a cost-benefit perspective.

Traditional Transformer Drying Methods
For many years, traditional methods have been the go-to approach for drying transformers, ensuring their longevity and reliability in electrical systems. Among the array of techniques employed, two common methods stand out: vacuum drying and oven drying.
1. Vacuum Drying:
Vacuum drying is a method that involves creating a vacuum within the transformer tank, effectively lowering the boiling point of water. This reduction in boiling point allows moisture trapped within the insulation to vaporize at lower temperatures, facilitating its removal. While undeniably effective in moisture extraction, vacuum drying is not without its drawbacks.
One significant downside is the time-consuming nature of the process. Depending on the size of the transformer, vacuum drying can take several days to complete, leading to prolonged downtime. Furthermore, the equipment required for vacuum drying is specialized and often expensive, adding to the overall complexity and cost of the procedure. Additionally, the expertise needed to operate this equipment further increases the barrier to entry for utilizing vacuum drying effectively.
2. Oven Drying:
Oven drying involves the removal of the transformer core and windings, which are then placed in a heated oven. The elevated temperature within the oven accelerates the evaporation of moisture from the insulation, effectively drying the transformer. However, like vacuum drying, oven drying comes with its set of challenges.
One notable concern with oven drying is the risk of overheating the insulation. Prolonged exposure to high temperatures can lead to thermal degradation and permanent damage to the transformer’s components. This potential for damage necessitates careful monitoring and control of temperature levels throughout the drying process to mitigate risks effectively.
Furthermore, the dismantling and reassembling of the transformer required for oven drying contribute to additional downtime and labor costs. The process of disassembly and reassembly is intricate and time-consuming, further extending the duration of the drying process and increasing associated expenses.
These traditional methods, while established, have limitations. They can be slow, energy-intensive, and potentially damaging to transformers.
Dry Air Generators for Transformer Drying

Dry air generators represent a modern and efficient approach to transformer drying, utilizing desiccant dehumidification technology to effectively remove moisture from transformer insulation. Unlike traditional methods that may involve silica gel breathers, vacuum drying, or nitrogen gas, dry air generators offer several distinct advantages.
Desiccant materials, commonly silica gel or molecular sieves, are hygroscopic, meaning they have a natural affinity for moisture and readily absorb it from the surrounding air. In dry air generators, these desiccants are used to create a dry air stream by absorbing moisture as air passes through them. This dry air is then circulated through the transformer tank, efficiently removing moisture from the insulation.
Advantages of Dry Air Generators:
- Faster Drying Times: One of the primary advantages of dry air generators is their ability to significantly reduce drying times compared to traditional methods. By circulating dry air directly through the transformer tank, moisture removal is accelerated, leading to shorter downtime and reduced maintenance costs.
- Lower Energy Consumption: Dry air generators typically consume less energy compared to traditional methods such as vacuum pumps or heating elements. The efficient desiccant dehumidification process requires minimal energy input, resulting in cost savings over the long term.
- Reduced Risk of Overheating: The controlled environment provided by dry air generators minimizes the risk of overheating the transformer’s insulation. Unlike vacuum drying, which involves heating the transformer oil to facilitate moisture evaporation, dry air generators maintain a stable and safe drying temperature, ensuring the integrity of the insulation material.
- Safer Operation: Dry air generators eliminate the need for high temperatures or vacuums, making the drying process inherently safer. Traditional methods may pose risks of overheating, equipment malfunction, or personnel injury. In contrast, dry air generators offer a safer and more controlled drying environment, enhancing overall operational safety.
By leveraging desiccant dehumidification technology, dry air generators offer a more efficient, cost-effective, and safer solution for transformer drying compared to traditional methods. With faster drying times, lower energy consumption, and reduced risk of overheating, dry air generators are increasingly becoming the preferred choice for ensuring the reliability and longevity of transformers in electrical systems.
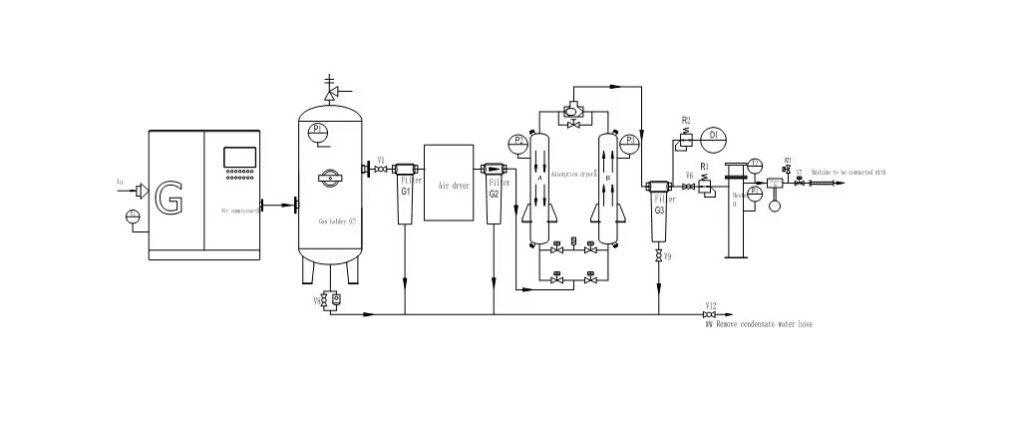
Cost-Benefit Analysis of Dry Air Generators and Traditional Transformer Drying Methods
When comparing the cost-effectiveness of dry air generators to traditional drying methods, it’s essential to consider various factors that impact both operational expenses and overall efficiency. Dry air generators offer a range of advantages that contribute to their cost-effectiveness compared to traditional methods such as silica gel breathers, vacuum drying, or nitrogen gas displacement.
1. Elimination of Recurring Expenses:
Dry air generators eliminate the need for recurring expenses associated with maintenance and replenishment of desiccant materials or nitrogen gas. Unlike silica gel breathers, which require regular replacement as they become saturated with moisture, dry air generators utilize desiccant beds that can be regenerated, reducing long-term operational costs. Similarly, the ongoing costs associated with nitrogen refills are eliminated, leading to significant savings over the lifespan of the equipment.
2. Efficiency and Speed of Drying Process:
Dry air generators offer faster drying times compared to traditional methods, resulting in reduced downtime and labor costs. By circulating dry air directly through the transformer tank, moisture removal is accelerated, allowing for quicker turnaround times during maintenance or servicing. This increased efficiency not only minimizes operational disruptions but also improves overall system reliability by ensuring prompt restoration of optimal transformer conditions.
3. Versatility and Portability:
Another factor contributing to the cost-effectiveness of dry air generators is their versatility and portability. Unlike traditional methods that may rely on external gas supplies or specialized equipment, dry air generators can be deployed in a wide range of environments, including remote or challenging locations. Their compact and portable design makes them suitable for on-site drying operations without the need for extensive infrastructure or logistical support. This accessibility reduces transportation costs and logistical complexities, making dry air generators a more practical and cost-effective solution for transformer drying, especially in situations where access to external resources may be limited.
In summary, dry air generators offer a cost-effective alternative to traditional drying methods for transformer maintenance and servicing. By eliminating recurring expenses, improving drying efficiency, and enhancing versatility and portability, dry air generators provide significant long-term savings while ensuring reliable and efficient operation of transformers in various applications. As the demand for reliable power distribution continues to grow, investing in modern drying technologies like dry air generators is essential for optimizing operational efficiency and minimizing lifecycle costs in electrical infrastructure management.
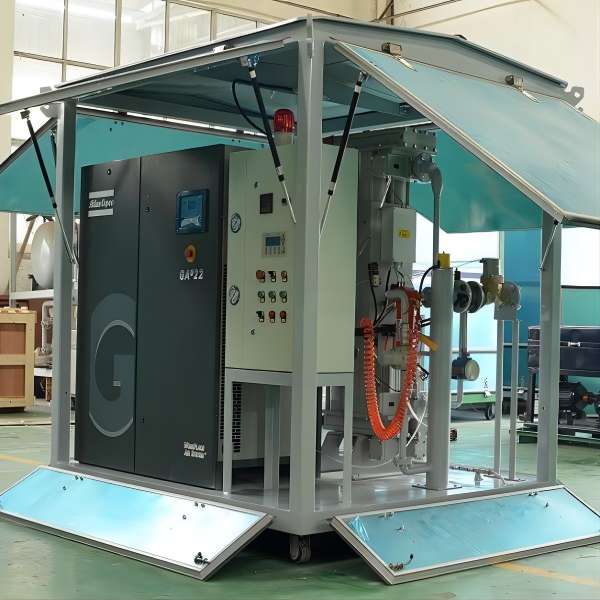

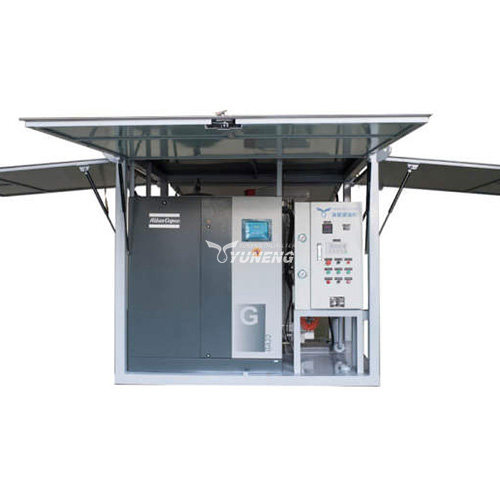
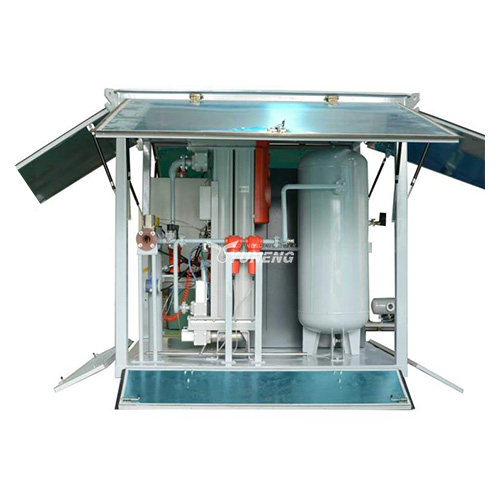
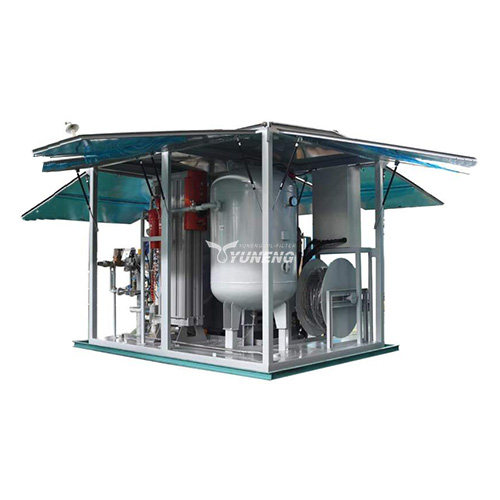
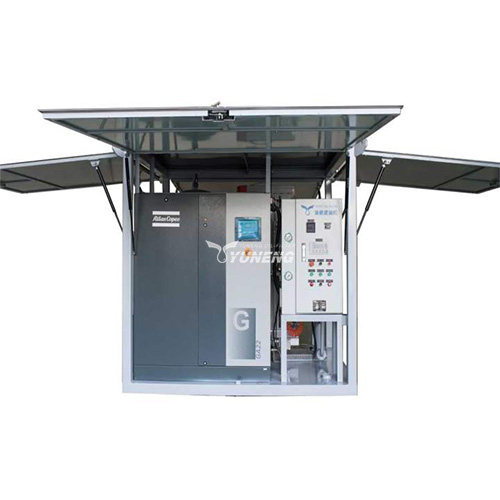
YUNENG GF Series Dry Air Generator
The YUNENG GF Series Dry Air Generator stands out as an innovative solution for transformer drying. Featuring advanced desiccant drying technology, precise control options, user-friendly interface, and compact design, it offers unmatched performance and efficiency.
- Advanced Desiccant Drying Technology: The GF Series utilizes high-quality desiccant materials to produce clean, dry air with low dew points, ensuring thorough moisture removal from transformers.
- Precise Control and Monitoring: Operators can easily adjust airflow, temperature, and humidity levels for optimal drying, aided by intuitive controls and real-time monitoring systems.
- Compact and Portable Design: Despite its advanced features, the GF Series boasts a compact and portable design, making it versatile for various applications and environments.
- Comprehensive Range of Models: With a range of models available, operators can choose the appropriate size and configuration to meet specific drying requirements.
- Reliability and Durability: Built for continuous operation, the GF Series ensures reliability and minimal downtime even in challenging conditions, offering peace of mind to operators.
In conclusion, the YUNENG GF Series Dry Air Generator offers a cost-effective and efficient solution for transformer drying, ensuring the longevity and reliability of electrical systems.
Conclusion
Traditional drying methods, while established, have limitations in terms of speed, energy consumption, and potential for damage. Dry air generators offer a faster, more efficient, and safer alternative with significant cost-benefit advantages. While the upfront cost may be higher, the operational savings, improved transformer health, and overall reliability make dry air generators a compelling choice for transformer drying in today’s world. As technology continues to develop, dry air generators are poised to play an increasingly important role in maintaining the health and efficiency of our power grids.







