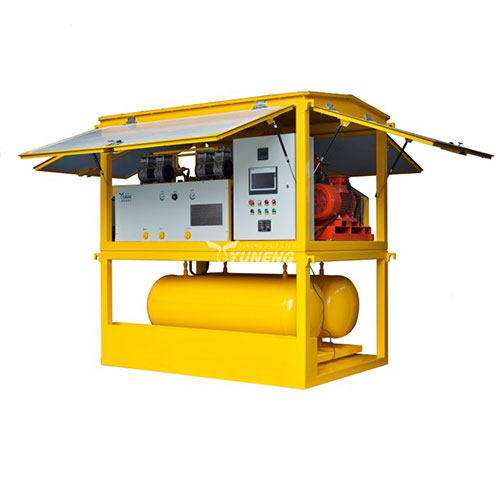
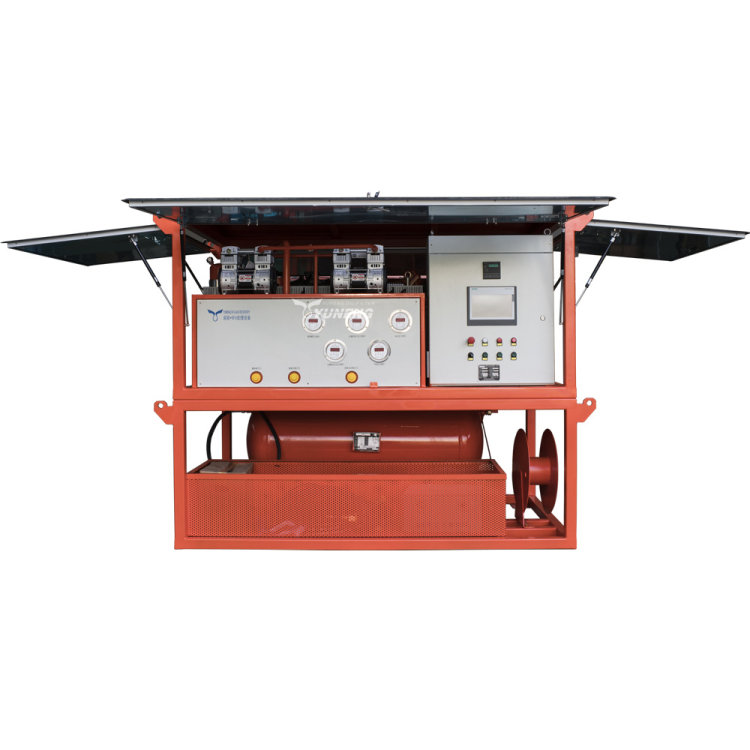
How to Ensure Purity and Performance in SF6 Gas Recovery?
Table of Contents
Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) is a highly effective insulating gas used extensively in electrical equipment such as circuit breakers and switchgear. Its remarkable electrical insulating properties make it indispensable in high-voltage applications. However, SF6 is also a potent greenhouse gas with a global warming potential much higher than carbon dioxide. Consequently, the recovery and recycling of SF6 gas have become crucial for environmental protection and regulatory compliance. This article explores the key aspects of ensuring the purity and performance of SF6 gas during the recovery process, focusing on its properties, the recovery process itself, and the testing of recovered gas.
Understanding SF6 Gas Properties
SF6 gas is known for its exceptional electrical insulating capabilities, making it the preferred choice for high-voltage equipment. Understanding its properties is essential for managing its recovery and recycling effectively.
Chemical and Physical Properties
SF6 is a colorless, odorless gas that is chemically inert under normal conditions. Its molecular structure consists of a sulfur atom surrounded by six fluorine atoms, creating a highly stable compound. This stability contributes to its effectiveness as an insulator but also means that it does not break down easily in the environment.
The gas has a high dielectric strength, which allows it to withstand high voltages without conducting electricity. This property is critical in preventing electrical discharges in switchgear and circuit breakers. SF6 also has excellent thermal and chemical stability, which ensures its performance over long periods and under varying conditions.
Usage and Applications
SF6 is primarily used in electrical equipment such as circuit breakers, transformers, and switchgear. Its ability to maintain high insulation levels while being compact and efficient makes it a preferred choice for modern electrical systems. Additionally, SF6 is used in various scientific and medical applications due to its unique properties.
Despite its advantages, SF6’s environmental impact has led to increased scrutiny and the development of regulations aimed at minimizing its release into the atmosphere. The need for effective recovery and recycling processes has become more pressing to mitigate its environmental footprint.
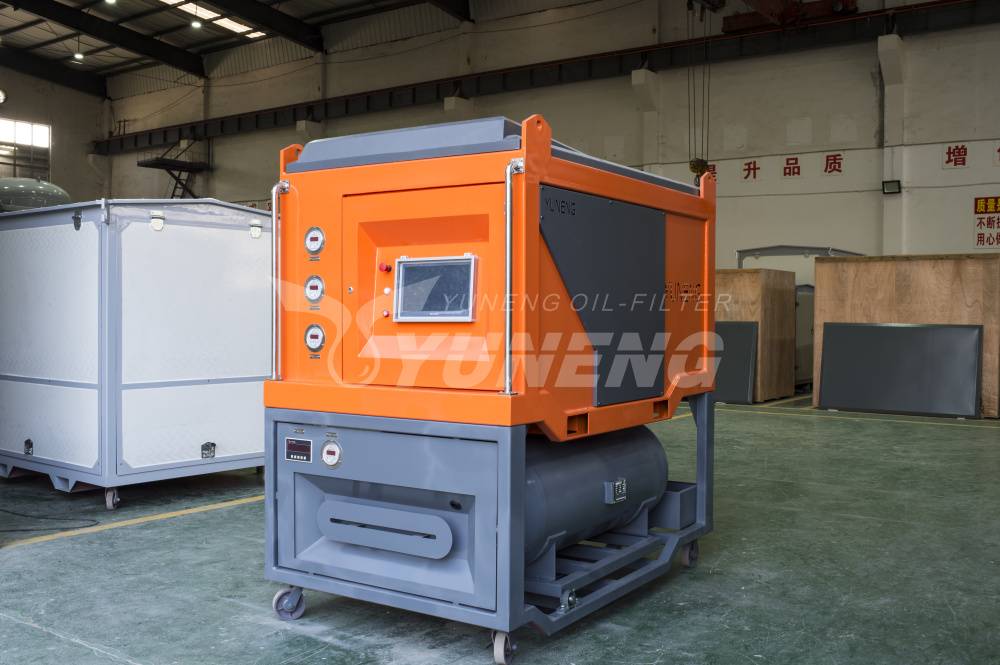

How to Recycle SF6 Gas with High Purity and Performance?
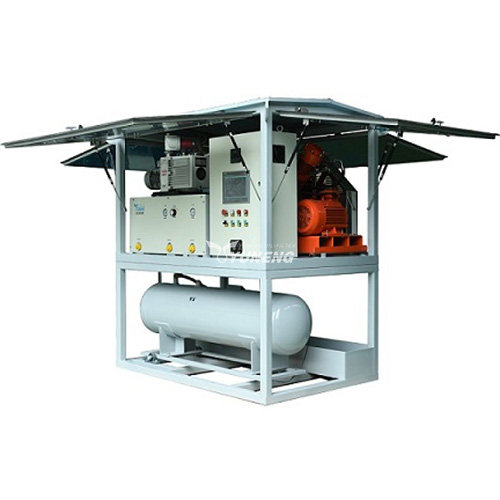
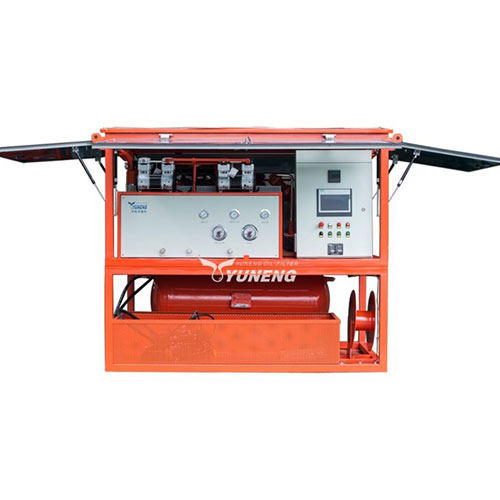
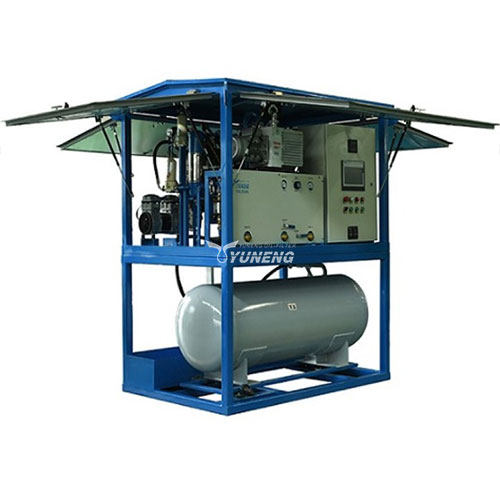
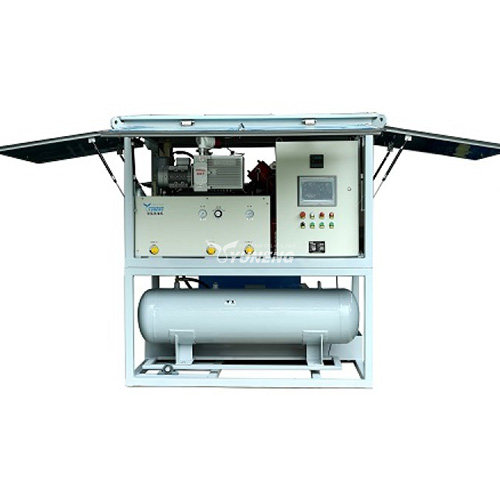
1. Advanced SF6 Gas Recovery Equipment
Effective recovery of SF6 gas relies on specialized equipment designed to handle its unique properties and high pressure. The main types of equipment used in SF6 gas recovery include:
- SF6 Gas Recovery Units: These portable units are equipped with compressors to capture SF6 gas from high-voltage equipment. They typically include filtration systems to remove particulate matter and contaminants before the gas is stored. Key features of these units often include pressure regulation, automatic shut-off mechanisms, and digital monitoring systems to ensure efficient and safe operation.
- SF6 Purifiers: Purification systems are critical for removing impurities and ensuring the recovered gas meets quality standards. These purifiers often use advanced adsorption materials such as activated alumina or molecular sieves to absorb moisture and chemical contaminants. Some purifiers are designed to handle specific types of impurities, such as byproducts formed during the use of SF6.
- Storage Tanks: Once recovered, SF6 gas is stored in high-pressure tanks designed to handle its unique characteristics. These tanks are constructed from materials resistant to corrosion and leakage, and they are equipped with monitoring systems to track pressure, temperature, and gas quality. Proper storage is essential to maintain the gas’s purity and prevent any loss or degradation.
2. What Technologies Are Used in the SF6 Gas Purification and Recovery Process?
The recovery and purification of SF6 gas involve several advanced technologies aimed at removing contaminants and ensuring the gas is suitable for reuse:
- Filtration Systems: These systems use fine filters and coalescers to remove solid particles and liquid contaminants from the gas. High-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters and coalescing filters are commonly used to ensure the gas is free from particulate matter that could affect its performance.
- Adsorption Technologies: Adsorption is used to remove trace amounts of impurities and moisture from SF6 gas. Materials such as activated carbon and silica gel are employed to capture these contaminants. In some systems, specialized adsorbents are used to target specific contaminants, such as sulfur dioxide or hydrogen fluoride, which can degrade the gas’s insulating properties.
- Chemical Scrubbing: This method involves the use of chemical reagents to neutralize or capture unwanted byproducts and contaminants. Chemical scrubbers are designed to handle specific types of impurities, such as decomposed SF6 or other gases that may form during the gas’s use. The scrubbers typically use solutions or solid reagents that react with contaminants to remove them from the gas stream.
3. Specific Steps in SF6 Gas Recovery
The SF6 gas recovery process is a multi-step procedure that ensures the gas is effectively captured, purified, and stored:
- Collection and Transport: SF6 gas is initially collected from electrical equipment using specialized recovery units. These units are connected to the equipment to extract the gas under controlled conditions. The collected gas is then transported to a recovery facility, often via pipelines or high-pressure containers, where it undergoes further processing.
- Filtration and Purification: At the recovery facility, the gas passes through filtration and purification systems. This step involves removing any particulate matter, moisture, and chemical contaminants to ensure the gas meets the required purity standards. The purification process may include multiple stages of filtration and adsorption, depending on the level of contamination.
- Storage and Handling: After purification, the SF6 gas is stored in high-pressure tanks designed to maintain its stability and purity. The storage tanks are equipped with monitoring systems to track the gas’s pressure, temperature, and overall condition. Proper handling procedures are followed to prevent leaks and ensure the safe storage of the gas until it is ready for reuse or recycling.
By employing advanced equipment and technologies, the SF6 gas recovery process can effectively manage and recycle this valuable gas while minimizing its environmental impact.
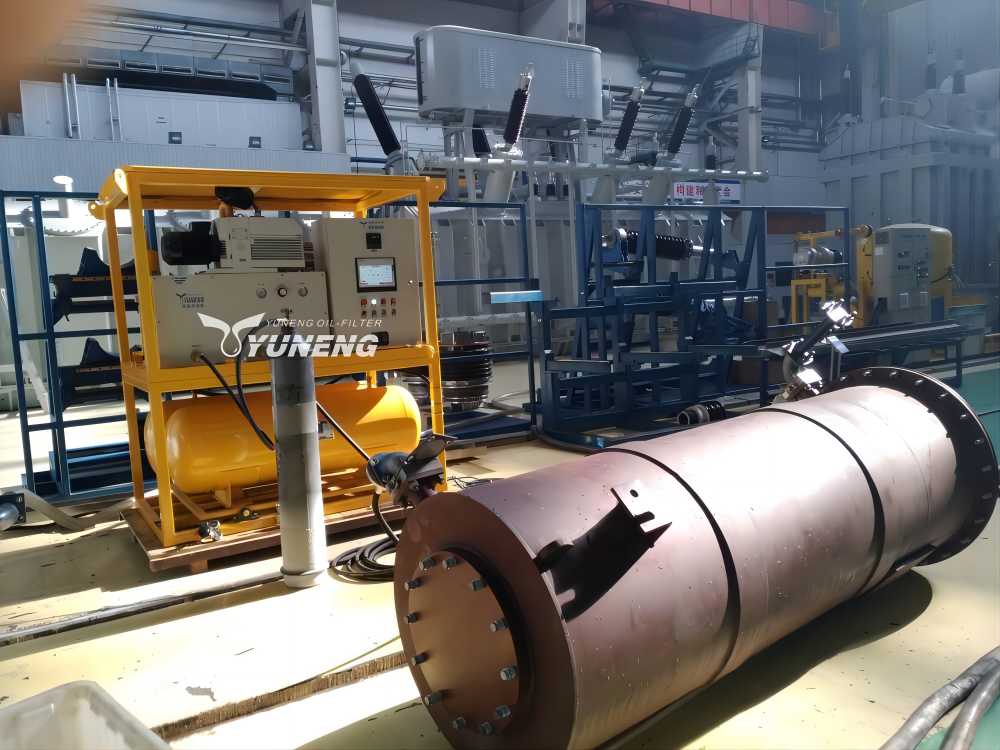

Post-Recovery SF6 Gas Purity and Performance Testing
1. Purity Testing Methods
To confirm the purity of recovered SF6 gas, various analytical techniques are used:
- Gas Chromatography: This method separates and analyzes compounds in a gas mixture. It can detect impurities at very low concentrations, ensuring the recovered SF6 meets purity standards.
- Infrared Spectroscopy: Infrared spectroscopy measures the absorption of infrared light by the gas. This technique helps identify and quantify specific contaminants present in SF6.
- Quality Standards: The purity of SF6 gas is often assessed against industry standards, such as those set by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) or other regulatory bodies. Compliance with these standards ensures the gas’s suitability for reuse.
2. Performance Evaluation
Evaluating the performance of recovered SF6 gas involves assessing its effectiveness as an insulating medium:
- Dielectric Strength Testing: This test measures the gas’s ability to withstand electrical stress without breaking down. High dielectric strength is crucial for ensuring the gas can perform effectively in electrical equipment.
- Leakage Testing: Ensuring that the recovered SF6 gas does not leak from storage cylinders or equipment is vital. Leakage testing involves checking for any signs of gas escape and addressing potential issues to maintain gas integrity.
- Reusability Assessment: The performance of recovered SF6 gas is also evaluated based on its ability to function effectively in electrical equipment. This includes assessing its insulating properties and ensuring it meets performance specifications.
Given the above, the recovery and recycling of SF6 gas are essential processes in the electrical industry, ensuring the purity and performance of SF6 gas during the recovery process is essential for both environmental protection and the efficient operation of electrical equipment. Through a thorough understanding of SF6 gas characteristics, the utilization of advanced recovery equipment, and rigorous quality control measures, the industry can maintain the integrity and performance of this critical component. As regulations become stricter and environmental concerns grow, the importance of SF6 gas recovery and recycling will only continue to increase, making it crucial for industries to adopt and refine these processes.






